1. Introduction
In this document, we will introduce the KDP2 architecture comprising new software(SW) and firmware(FW) design for KL520.
In comparison with the previous SW/FW architecture, this aims to simplify the design flow for AI applications development.
When referring to a complete AI application development, actually three parts are involved:
- model development
- software development
- firmware development
Below diagram depicts three parts of development in a big picture.
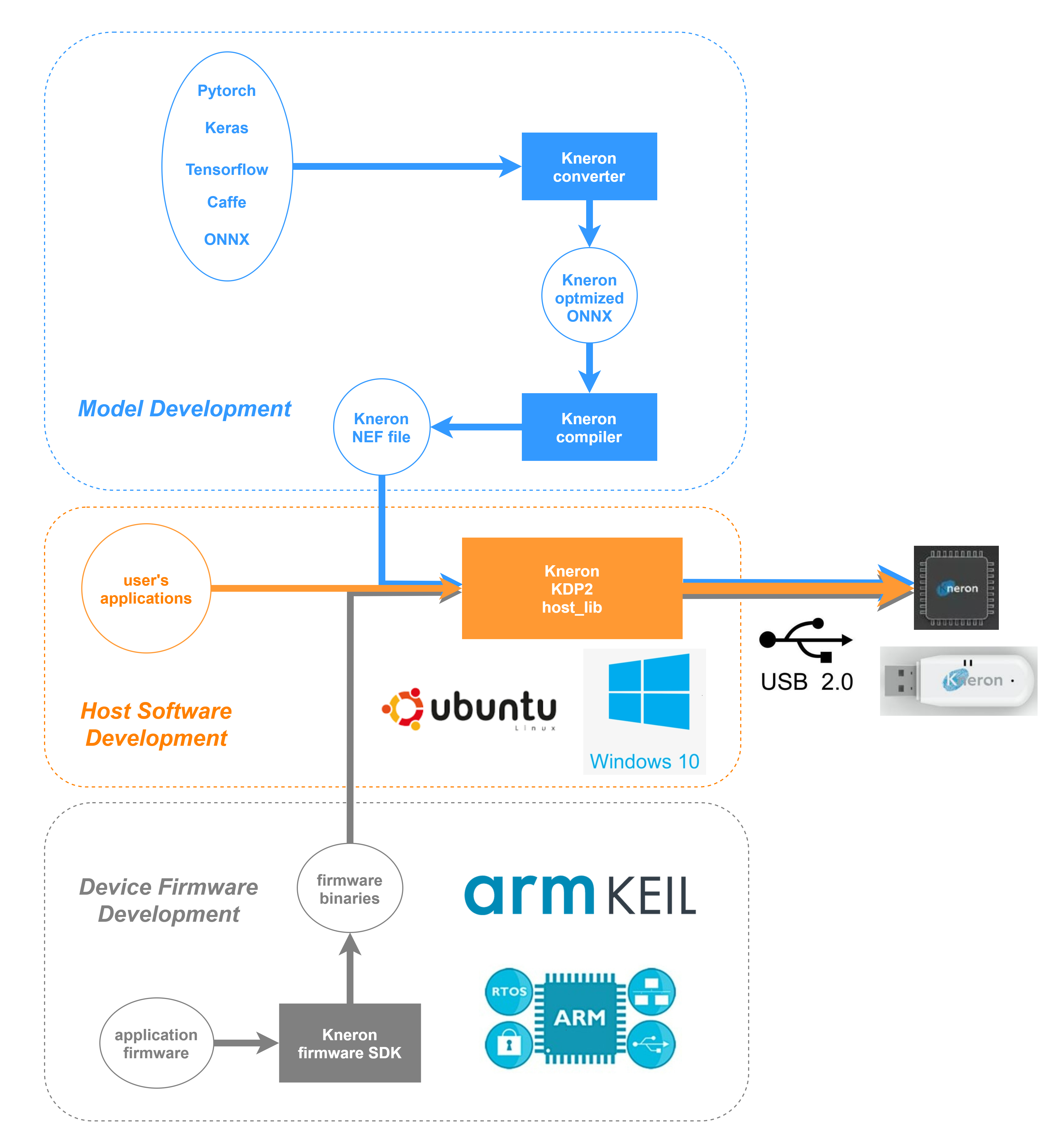
This Getting Started document only focuses on host software usage with the AI dongle to perform following functionality.
- How to build the host software.
- How to update firmware to the AI dongle.
- How to connect AI dongles.
- How to run the APP inference example.
- How to run the generic inference example.
For model development, please refer to the Toolchain Docker part.
For firmware development, it is more advanced, please contact Kneron.
Below gives some definitions regarding the KDP2 host_lib:
-
host_lib is a software library developed by Kneron and it allows users to manipulate the AI dongle through sophisticated C/C++/Python API.
-
KDP2 API is part of the host_lib written in C and it provides simplied functions and examples to help users develop their software applications.
-
NEF represents for NPU Executable Format which may comprise one or multiple models and it can only work on Kneron's SoC. The host_lib comes with some NEFs for demonstration purposes. We will use the Tiny Yolo v3 NEF as the model input in our inference examples.
-
Firmware is the code responsible for driving Kneron SoC and make it work with the host_lib. The KDP2 firmware can work with the KDP2 host_lib and it has prebuilt images included in the host_lib.
host_lib (after v0.9.0) contains KDP2 software code and examples, prebuilt KDP2 firmware and some demonstrative NEF files; and with the AI dongle it can give some edge AI examples.
Here we will demonstrate below diagram scenario with followings:
- A host running Ubuntu
- One Kneron AI dongle.
- The host_lib package.
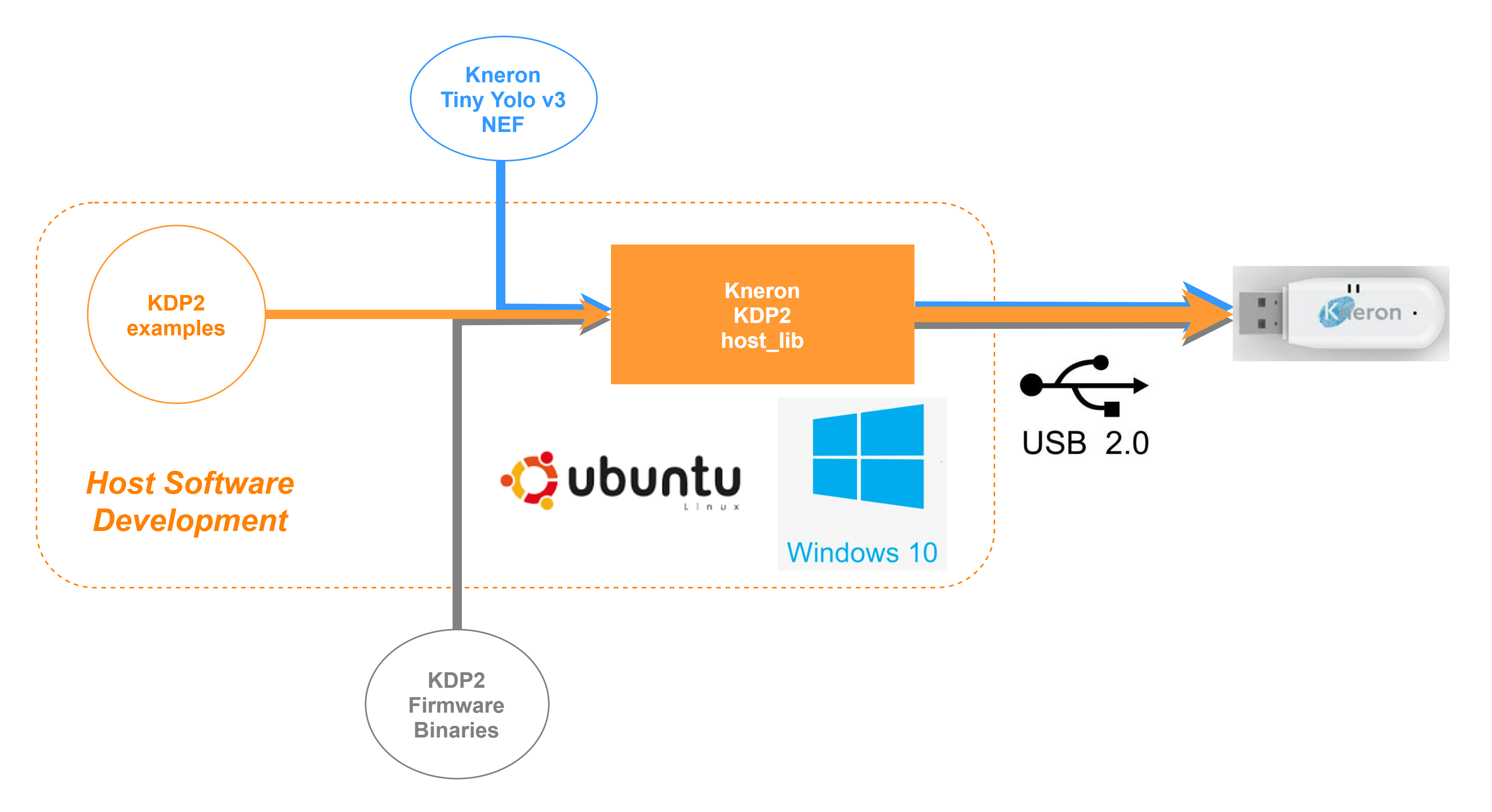
2. Build host_lib
*Note: here we use Linux-based OS Ubuntu.
Download the latest host_lib_vXXX.zip (after v0.9.0) into Ubuntu from https://www.kneron.com/tw/support/developers/, it is located at KNEON Stem(USB Dongle)/host_lib/.
Before building code, some build tools and packages must be set up for the first time.
Install CMake, libusb-1.0.0-dev and build-essential.
$ sudo apt install cmake
$ sudo apt install libusb-1.0-0-dev
$ sudo apt install build-essential
Decompress the host_lib_v0.9.0.zip. (or after v0.9.0)
$ unzip host_lib_v0.9.0.zip
Build code.
$ cd host_lib/
$ mkdir build ; cd build/
$ cmake ..
$ make -j
Once build is done, the libkdp2.so will be in build/kdp2/src/
Example executables will be in build/bin_kdp2/
Check if KDP2 examples are built successuflly.
$ ls bin_kdp2/
ex_kdp2_connect_test
ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw
ex_kdp2_update_firmware
ex_kdp2_scan_devices
...You should see some executables named in prefix 'kdp2_'.
3. Update firmware
Before running KDP2 examples, users need to make the AI dongle running with the KDP2 firmware.
Plug the AI dongle in the Ubuntu host and confirm it with the 'lsusb' command.
$ lsusb
...
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 3231:0100
...
If not seeing "3231:0100" (represents KL520 device), it may have a connectivity problem or some device failures.
Kneron provides different firmware for different applications on KL520.
It needs the KDP2 firmware to work with the host_lib KDP2 API; the firmware binaries are located at app_binaries/KL520/kdp2/.
Update the AI donge with the KDP2 firmware by the 'ex_kdp2_update_firmware'.
For multiple dongles, users can specify which device to be updated by the '-s' parameter.
$ cd bin_kdp2/
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_update_firmware
-h : help
-s : [device index] = '1'
-p : [firmware folder path] = '../../app_binaries/KL520/kdp2/'
start to update SCPU and NCPU firmwares to the device with port_path = 1-1
update SCPU firmware from file ../../app_binaries/KL520/kdp2//fw_scpu.bin
update SCPU firmware OK
update NCPU firmware from file ../../app_binaries/KL520/kdp2//fw_ncpu.bin
update NCPU firmware OK
4. Connect device tests
While one or multiple AI dongles are plugged into the host, they can be scanned to get some basic device information.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_scan_devices
scanning kneron devices ...
number of Kneron devices found: 2
listing devices infomation as follows:
[1] scan_index: '1'
[1] product_id: '0x100' (KL520)
[1] USB link speed: 'High-Speed'
[1] USB port path: '1-2'
[1] kn_number: '0xC506203C'
[1] Connectable: 'True'
[2] scan_index: '2'
[2] product_id: '0x100' (KL520)
[2] USB link speed: 'High-Speed'
[2] USB port path: '1-1'
[2] kn_number: '0xCC0A282C'
[2] Connectable: 'True'
Above shows that it founds two KL520 devices, a brief descript listed below.
- scan_index : An index number represents the device in the scanned order, can be used by KDP2 API to establish USB connection.
- product_id : The product ID.
- USB link speed : USB link speed, High-Speed is fastest speed for USB2.0.
- USB port path : This means the physical USB port path on the host.
- kn_number : Kneron's serial number for the device.
- Connectable : It tells if this device is connectable; one device can only be connected by one program at the same time.
The 'ex_kdp2_connect_test' can be used to test device connection, and it needs parameters for selecing the way to connect a Kneron device.
Normally we use the scan index.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_connect_test
usage:
./ex_kdp2_connect_test -s [device scan index] (can be known by kdp2_scan_devices())
./ex_kdp2_connect_test -p [product_name] (KL520, KL720 or after)
./ex_kdp2_connect_test -k [kn_number] (ex: 0x7F1A0000)
For example, use '-s 1' to connect the first scanned device.
It device is connectable, it will make a connection to it and then pause until pressing 'enter'.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_connect_test -s 1
connecting to device by scan_index = 1 ...
[1] scan_index: '1'
[1] product_id: '0x100' (KL520)
[1] USB link speed: 'High-Speed'
[1] USB port path: '1-2'
[1] kn_number: '0xC506203C'
>> press 'enter' to disconnect the device ...
disconnecting device ...
5. Run inference examples
The KDP2 host_lib provides two categories of API set for model inference.
One is the 'APP inference' category, providing some decent functions for specific applications with specified NEF models and it is designed to be used in a easy way.
Another is the 'Generic inference' category which is intended for advanced users who are interested in developing their models and implement corresponding post-processing code.
Below will demonstrate both usage in two examples.
App inference example
The 'ex_kdp2_tiny_yolo_v3' example utilizes the APP inference API and the Tiny Yolo V3 model to perform object detection.
When no parameters, it takes input_models/KL520/tiny_yolo_v3/models_520.nef as the inference model, input_images/street_cars_bike.bmp as the input image in BMP format and repeats 20 loops to calculate performance then prints inference results.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_tiny_yolo_v3
-h : help
-s : [device index] = '1'
-i : [image file path] (.bmp 24bits) = '../../input_images/street_cars_bike.bmp'
-l : [test loops] = '20'
image resolution 752x504, format RGB565
(device will convert it to 224x224, RGBA8888, only support downscaling)
starting doing inference, loop = 20
....................
total inference 20 images
time spent: 1.96 secs, FPS = 10.2
box count : 4
Box 0 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 298.0, 161.0, 422.0, 392.0, 0.904121, 0
Box 1 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 11.0, 171.0, 57.0, 299.0, 0.256544, 0
Box 2 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 447.0, 176.0, 719.0, 370.0, 0.987464, 2
Box 3 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 39.0, 178.0, 311.0, 372.0, 0.976890, 2
drew bounding box(es) on './ex_kdp2_tiny_yolo_v3.bmp'
disconnecting device ...
Besides output results in the screen console, it also draws detected objects in a new-created ex_kdp2_tiny_yolo_v3.bmp.

The key features of APP inference are listed below: - Specified model NEF. - Normally post-process is done in SoC. - Simplfied function parameters.
Generic inference example
Generic inference API is intended for users who have their own models and applications.
It needs more complex input parameters and normally the post-process is implemented by users in host side.
The 'ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw' is an example for showing how it work.
By default, it runs with a Tiny Yolo v3 model NEF and takes an BMP image as input and does post-process in host side.
Below shortly explains the key input parameters:
- model file path : NEF file path, it can be changed to user's own NEF.
- image file path : An image file path in BMP format. The actual input format for now supported is RGB565 or RGBA8888.
- inference model ID : The model ID of one model in the NEF. Each model should have a unique ID.
- image format : This indicates what image format preferred to be converted, the example converts BMP to RGB565 or RGBA888.
- normalize mode : Normalize mode depends how data is normalized when training the model.
- post process : In KDP2 we provide a few post-processing functions, if choosing 'yolo_v3' it use an internal post-processing function for processing yolo_v3 and outputs bounding boxes. For other models, users can use 'bypass' to diretly get floating point values of each output node.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw
-h : help
-s : [device index] = '1'
-m : [model file path] (.nef) = '../../input_models/KL520/tiny_yolo_v3/models_520.nef'
-i : [image file path] (.bmp 24bits) = '../../input_images/one_bike_many_cars_224x224.bmp'
-d : [inference model ID] = '19'
-c : [image format] (RGB565, RGBA8888) = 'RGB565'
-n : [normalize mode] ('none', '0_1', '-0.5_0.5', '-1_1') = '-0.5_0.5'
-p : [post process] ('bypass', 'yolo_v3') = 'yolo_v3'
-l : [test loops] = '20'
connect device ... OK
load model(s) ... OK
time spent: 0.57 secs
this NEF contains 1 model(s):
[1] model ID = 19
[1] model raw input width = 224
[1] model raw input height = 224
[1] model input channel = 3
[1] model raw image format = RGBA8888
[1] model raw output size = 430224
target inference model ID : 19
allocate memory 430224 bytes for RAW output
image resolution 224x224, format RGB565
(device will convert it to 224x224, RGBA8888, only support downscaling)
starting doing inference, loop = 20
....................
total inference 20 images
time spent: 0.71 secs, FPS = 28.2
================== [Post Process] 'yolo_v3' =========================
class count : 80
box count : 6
Box 0 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 104.0, 78.0, 141.0, 217.0, 0.949131, 0
Box 1 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 106.0, 145.0, 137.0, 214.0, 0.253075, 1
Box 2 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 35.0, 49.0, 131.0, 118.0, 0.989020, 2
Box 3 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 199.0, 48.0, 221.0, 131.0, 0.916225, 2
Box 4 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 129.0, 46.0, 197.0, 95.0, 0.887819, 2
Box 5 (x1, y1, x2, y2, score, class) = 12.0, 30.0, 64.0, 79.0, 0.618796, 2
drew bounding box(es) on './ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw.bmp'
===========================================================================
disconnecting device ...
From the console output, it can be observed that the information of models in the NEF is printed, including model ID, raw resolution, intput channel, raw image format and raw output size.
Raw output size indicates that a buffer of the size should be prepared to receive the output directly from the AI dongle, and it cannot be used until converting the raw output to well-structed floating point values.
If [post process] is set to 'yolo_v3', it draws detected objects in a new-created ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw.bmp.
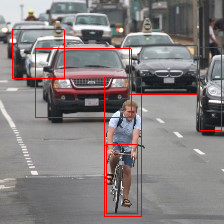
Otherwise if [post process] is set to 'bypass', the example dumps floating point values into .txt files for each output node.
$ sudo ./ex_kdp2_generic_inference_raw -p bypass
-h : help
-s : [device index] = '1'
-m : [model file path] (.nef) = '../../input_models/KL520/tiny_yolo_v3/models_520.nef'
-i : [image file path] (.bmp 24bits) = '../../input_images/one_bike_many_cars_224x224.bmp'
-d : [inference model ID] = '19'
-c : [image format] (RGB565, RGBA8888) = 'RGB565'
-n : [normalize mode] ('none', '0_1', '-0.5_0.5', '-1_1') = '-0.5_0.5'
-p : [post process] ('bypass', 'yolo_v3') = 'bypass'
-l : [test loops] = '20'
connect device ... OK
load model(s) ... OK
time spent: 0.48 secs
this NEF contains 1 model(s):
[1] model ID = 19
[1] model raw input width = 224
[1] model raw input height = 224
[1] model input channel = 3
[1] model raw image format = RGBA8888
[1] model raw output size = 430224
target inference model ID : 19
allocate memory 430224 bytes for RAW output
image resolution 224x224, format RGB565
(device will convert it to 224x224, RGBA8888, only support downscaling)
starting doing inference, loop = 20
....................
total inference 20 images
time spent: 0.53 secs, FPS = 37.6
================== [Post Process] 'bypass' =========================
number of output node : 2
node 0:
width: 7:
height: 7:
channel: 255:
number of data (float): 12495:
first 20 data:
1.699, 0.340, -0.170, -0.340, -0.340, -0.340,
-1.019, 1.189, 1.189, 0.679, 0.510,
0.340, 0.340, 0.510, -0.170, 0.000,
0.170, 0.170, 0.170, 0.000,
node 1:
width: 14:
height: 14:
channel: 255:
number of data (float): 49980:
first 20 data:
1.048, 0.000, -0.699, 1.048, 0.175, -0.175,
0.349, -0.175, 0.349, -0.524, 0.175,
-0.175, 0.000, -0.349, 1.573, 1.223,
0.699, 0.874, 0.699, 0.349,
dumped node 0 output to 'node0_7x7x255.txt'
dumped node 1 output to 'node1_14x14x255.txt'
===========================================================================
disconnecting device ...
For example, 'node0_7x7x255.txt' represents node 0, width x height x channel = 7x7x255, and its content looks like below.
1.699, 0.340, -0.170, -0.340, -0.340, -0.340, -1.019, 1.189, 1.189, 0.679, 0.510, 0.340, 0.340, 0.510, -0.170, 0.000, 0.170, 0.170, 0.170, 0.000, -0.340, -0.340, -0.679, -0.679, -0.849, -0.679, -0.510, 0.000, -7.984, -4.586, -4.247, -4.586, -5.266, -5.266, -8.153, -2.718, -4.416, -4.416, -4.077, -3.397, -3.737, -3.058, -6.115, -7.984, -8.833, -8.663, -9.003, -9.682, -8.323, -1.019, -1.019, -1.529, -1.529, -1.869, -3.227, -4.077, -5.096, -6.115, -7.304, -6.964, -7.304, -8.323, -8.153, -7.304, -10.192, -10.701, -10.022, -9.512, -8.153, -6.285, -1.529, -1.359, -1.189, -1.019, -0.510, 0.170, 0.170, -5.266, -7.134, -7.474, -6.795, -6.625, -5.606, -4.416, 0.340, 0.679, 0.510, -0.170, -0.679, -0.679, -0.510, -7.474, -10.192, -11.041, -10.192, -10.192, -8.833, -6.625, -5.775, -7.134, -6.625, -5.775, -5.436, -5.096, -5.096, -7.304, -9.512, -10.362, -9.852, -9.512, -9.512, -8.323, -9.173, -10.362, -10.532, -9.852, -9.512, -8.663, -7.644, -7.984, -9.512, -9.512, -8.833, -8.493, -8.493, -7.814, -5.606, -6.964, -6.625, -6.115, -6.285, -6.625, -6.115, -8.663, -11.041, -11.721, -10.871, -10.871, -10.871, -9.343, -8.663, -9.852, -9.682, -9.343, -9.173, -10.022, -9.682, -7.474, -8.833, -9.003, -8.833, -8.663, -9.852, -9.512, -9.003, -11.551, -12.230, -11.551, -11.721, -11.211, -9.343, -8.323, -10.022, -10.701, -10.192, -9.852, -9.512, -8.493, -8.663, -9.682, -10.022, -9.512, -10.022, -10.022, -9.003, -6.964, -7.304, -7.134, -6.964, -6.795, -7.304, -6.795, -8.153, -9.343, -9.682, -9.173, -9.512, -10.022, -9.512, -7.474, -9.512, -10.701, -10.022, -10.532, -10.022, -8.493, -5.775, -7.474, -7.814, -6.795, -6.795, -6.795, -5.096, -8.663, -10.701, -11.041, -10.701, -9.852, -9.682, -9.003, -6.115, -8.493, -8.493, -7.984, -6.964, -5.436, -3.907, -8.663, -10.362, -10.362, -9.852, -9.003, -8.493, -7.304, -9.003, -10.192, -10.532, -9.512, -9.512, -10.192, -10.362, -7.984, -10.532, -10.701, -10.192, -9.173, -8.663, -7.644, -11.041, -12.740, -12.910, -12.570, -12.060, -11.721, -10.532, -7.644, -10.362, -11.381, -11.041, -10.532, -10.871, -10.022, -8.493, -11.211, -11.381, -10.362, -11.041, -11.041, -9.852, -7.814, -9.512, -10.022, -9.512, -8.663, -8.663, -7.814, -6.795, -9.512, -10.022, -9.343, -9.343, -8.663, -7.134, -8.833, -10.871, -11.211, -11.041, -10.701, -10.192, -9.003, -9.852, -11.551, -13.080, -12.400, -11.890, -11.721, -10.701, -8.323, -10.532, -10.701, -10.362, -10.362, -9.852, -9.003, -10.192, -12.570, -12.400, -11.721, -11.721, -11.551, -9.682, -8.153, -10.532, -11.041, -10.701, -10.192, -10.022, -8.323, -7.474, -9.173, -9.343, -8.323, -7.984, -7.814, -7.304, -9.173, -11.551, -12.740, -11.721, -11.041, -10.192, -8.153, -9.343, -11.890, -12.740, -11.721, -11.211, -10.362, -8.493, -8.153, -10.701, -11.381, -10.362, -10.022, -9.512, -8.663, -8.493, -10.362, -10.362, -9.343, -9.003, -8.663, -7.814, -9.003, -11.211, -11.721, -10.701, -10.701, -10.532, -9.512, -9.852, -10.022, -9.852, -9.343, -9.512, -9.003, -8.323, -9.682, -12.060, -12.400, -11.890, -11.381, -10.871, -9.852, -8.663, -10.192, -10.532, -10.192, -9.512, -9.173, -8.493, -10.532, -12.400, -12.400, -11.721, -10.701, -10.192, -8.833, -7.304, -9.173, -9.512, -8.663, -7.814, -7.474, -6.795, -5.945, -6.964, -6.795, -6.455, -5.945, -6.625, -6.455, -7.644, -9.343, -9.512, -9.173, -8.663, -7.814, -7.474, -10.871, -12.910, -13.419, -12.570, -11.721, -10.532, -9.852, -10.701, -12.570, -12.740, -12.400, -11.890, -11.551, -10.022, -7.304, -8.663, -9.682, -8.833, -8.323, -8.153, -7.304, -10.701, -12.910, -13.080, -12.400, -11.381, -11.041, -9.512, -7.304, -9.852, -9.343, -8.323, -7.984, -7.984, -6.964, -8.493, -10.701, -10.362, -9.852, -9.512, -9.682, -8.663, -4.756, -6.625, -6.625, -5.606, -4.416, -5.096, -4.416, -9.852, -11.551, -11.890, -11.041, -10.701, -10.871, -9.852, -8.323, -10.532, -9.682, -8.833, -8.833, -9.512, -8.323, -8.153, -10.022, -10.022, -8.833, -8.323, -8.323, -7.814, -8.153, -10.362, -10.022, -9.343, -8.833, -7.984, -6.455, -9.682, -11.551, -11.211, -10.871, -10.362, -9.512, -8.323, -10.532, -12.400, -12.910, -12.400, -11.721, -11.381, -10.532, -9.343, -11.890, -12.230, -11.551, -11.211, -10.532, -9.512, -8.663, -10.532, -10.192, -9.852, -9.173, -8.833, -8.153, -9.173, -10.532, -11.041, -10.362, -10.022, -8.833, -8.323, -7.984, -8.663, -8.323, -8.323, -8.153, -7.814, -6.795, -7.814, -8.833, -8.663, -8.323, -8.153, -8.153, -7.474, -9.852, -10.192, -10.362, -9.852, -9.682, -9.343, -8.663, -9.682, -11.551, -11.211, -10.532, -10.022, -10.022, -8.833, -7.304, -9.173, -8.493, -7.814, -7.304, -6.625, -5.096, -7.984, -9.852, -10.022, -9.512, -9.512, -9.343, -8.153, -9.003, -10.701, -11.381, -10.701, -10.871, -9.852, -8.153, -9.173, -11.041, -11.381, -10.192, -9.173, -9.003, -7.474, -9.003, -10.871, -11.381, -10.362, -10.022, -9.852, -9.343, -8.323, -10.022, -10.362, -10.022, -9.512, -10.192, -9.512, -10.362, -11.381, -11.721, -11.041, -10.701, -10.701, -10.192, -11.041, -12.910, -12.740, -12.060, -11.381, -11.211, -10.701, -0.170, 0.170, -0.340, -0.679, -0.340, -0.679, -0.170, 0.000, 0.510, 0.849, 0.849, 0.849, 0.510, 0.340, -0.170, 0.340, 0.340, 0.510, 0.510, 0.170, -0.510, -0.510, -0.679, -0.679, -0.679 ....