2. Toolchain Deployment
Review the system requirements below before start installing and using the toolchain.
2.1. System requirements
- Hardware: Minimum quad-core CPU, 4GB RAM and 6GB free disk space.
- Operating system: Window 10 x64 version 1903 or higher with build 18362 or higher. Ubuntu 16.04 x64 or higher. Other OS which can run docker later than 19.03 may also work. But they are not tested. Please take the risk yourself.
- Docker: Docker Desktop later than 19.03. Here is a link to download Docker Desktop.
TIPS:
For Windows 10 users, we recommend using docker with wsl2, which is Windows subsystem Linux provided by Microsoft. Here is how to install wsl2 and how to install and run docker with wsl2. Also, you might to want to adjust the resources docker use to ensure the tools' normal usage. Please check the FAQ at the end of this document on how to do that.
Please double-check whether the docker is successfully installed and callable from the console before going on to the next section. If there is any problem about the docker installation, please search online or go to the docker community for further support. The questions about the docker is beyond the reach of this document.
2.2. Pull the latest toolchain image
All the following steps are on the command line. Please make sure you have the access to it.
TIPS:
You may need
sudoto run the docker commands, which depends on your system configuration.
You can use the following command to pull the latest toolchain docker.
docker pull kneron/toolchain:latestNote that the latest toolchain version v0.26.0. You can find the version of the toolchain in
/workspace/version.txt inside the docker. If you find your toolchain is earlier than v0.26.0, you may need to find the
document from the manual history.
2.3. Toolchain Docker Overview
After pulling the desired toolchain, now we can start walking through the process. In all the following sections, we use
kneron/toolchain:latest as the docker image. Before we actually start the docker, we'd better provide a folder
which contains the model files you want to test in our docker, for example, /mnt/docker. Then, we can use the
following command to start the docker and work in the docker environment:
docker run --rm -it -v /mnt/docker:/docker_mount kneron/toolchain:latestTIPS:
The mount folder path here is recommended to be an absolute path.
Here are the brief explanations for the flags. For detailed explanations, please visit docker documents.
--rm: the container will be removed after it exists. Each time we usedocker run, we create a new docker container. Thus, without this flag, the docker will consumes more and more disk space.-it: enter the interactive mode so we can use the bash.-v: mount a folder into the docker container. Thus, we can visit the desired files from the host and save the result from the container.
2.3.1. Folder structure
After logging into the container, you are under /workspace, where all the tools are. Here is the folder structure and
their usage:
/workspace
|-- E2E_Simulator # End to end simulator
|-- ai_training # AI training project.
|-- cmake # Environment
|-- examples # Example for the workflow, will be used later.
|-- libs # The libraries
| |-- ONNX_Convertor # ONNX Converters and optimizer scripts, will be discussed in section 3.
| |-- c_sim_[version] # Hardware simulators for specific hardware versions.
| |-- compiler # Compiler for the hardware and the IP evaluator to infer the performance.
| |-- dynasty # Simulator which only simulates the calculation.
| `-- fpAnalyser # Analyze the model and provide fixed point information.
|-- miniconda # Environment
|-- scripts # Scripts to run the tools, will be discussed in section 3.
|-- webgui # Web GUI for the toolchain. Please check appendix for details.
`-- version.txt2.4. FAQ
2.4.1. How to adjust the system resources usage of the docker?
To ensure the quantization tool can work, we recommend the docker has at least 4GB of memory. The actual required size depends on your model size and the image number of quantization.
For Linux uses, by default, docker can share all the CPU and memory resouces of their host machine. So, this isn't a problem. But for Windows users, not like Linux, the system resources are not shared. User might want to adjust the resources usage by themselves.
For the docker based on wsl2, as we recommended in the section 1 of this document, it can use update to 50% of your total system memory and all the CPU resources. And here is a artical introduce how to manage the system resources used by wsl2.
For the docker based on wsl, users can find the management of the system resouces directly in the setting of the docker.
For the docker toolbox, it is actually based on the VirtualBox virtual machine. So, user need find which virtual machine the docker is using first. User need to start the docker terminal to ensure the docker is running before we start. And here is following precedue
- Open the VirtualBox management tool.
Figure FAQ3.1 VirtualBox
- Check the status. There should be only one virtual machine running if there is no other virtual machines started manually by the user.
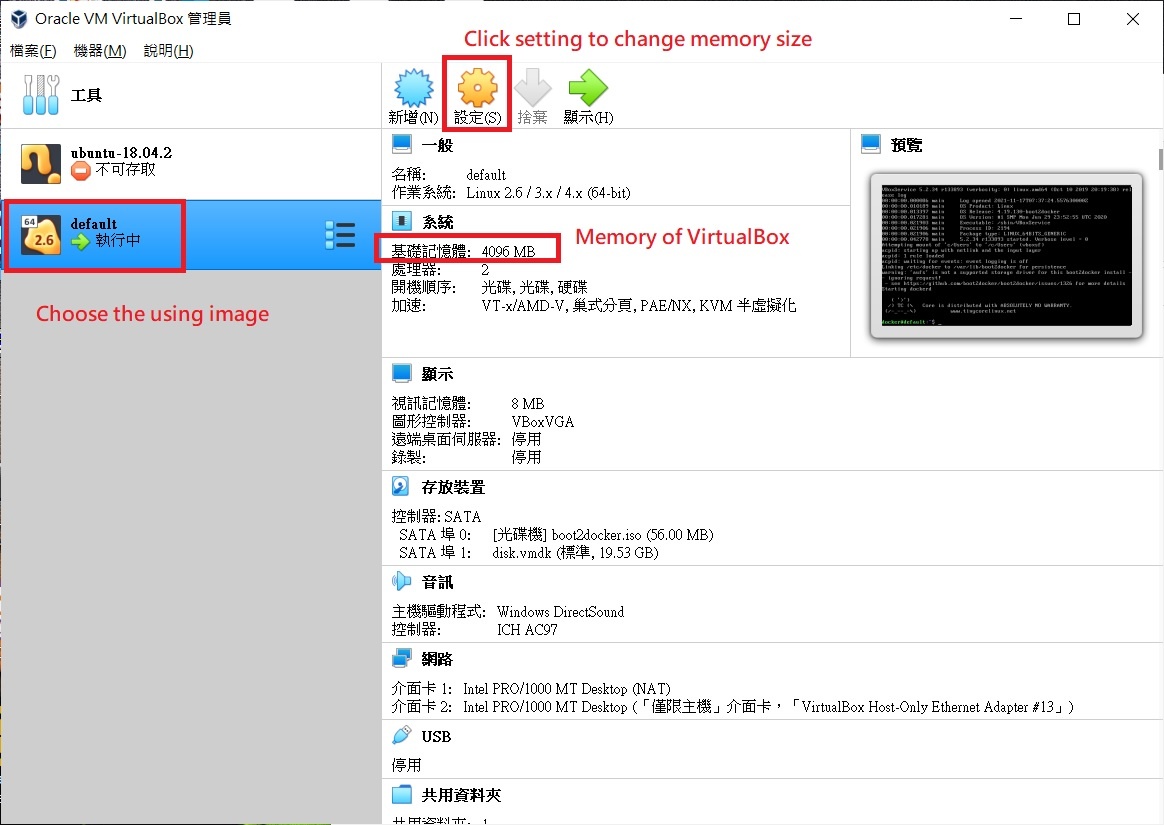
Figure FAQ3.2 VM status
- Close the docker terminal and shutdown the virtual machine before we adjust the resources usage.
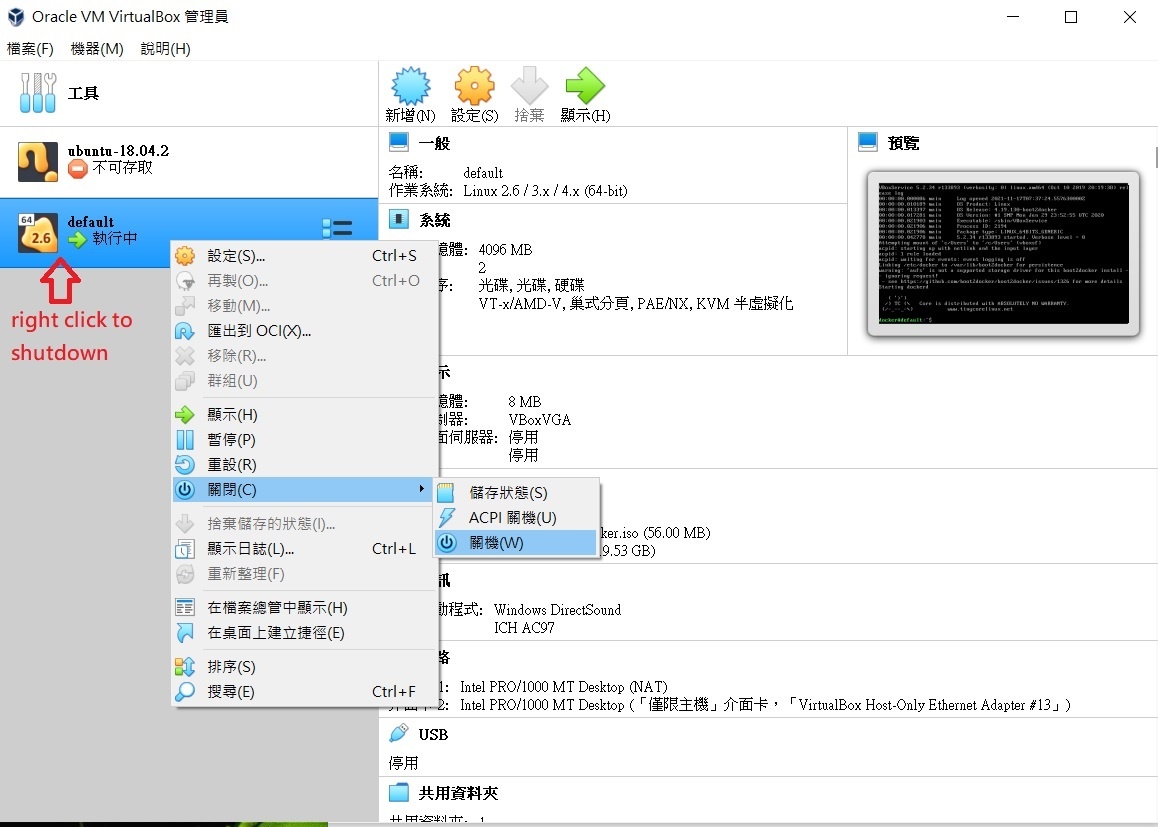
Figure FAQ3.3 VM shutdown
- Adjust the memory usage in the virtual machine settings. You can also change the cpu count here as well.
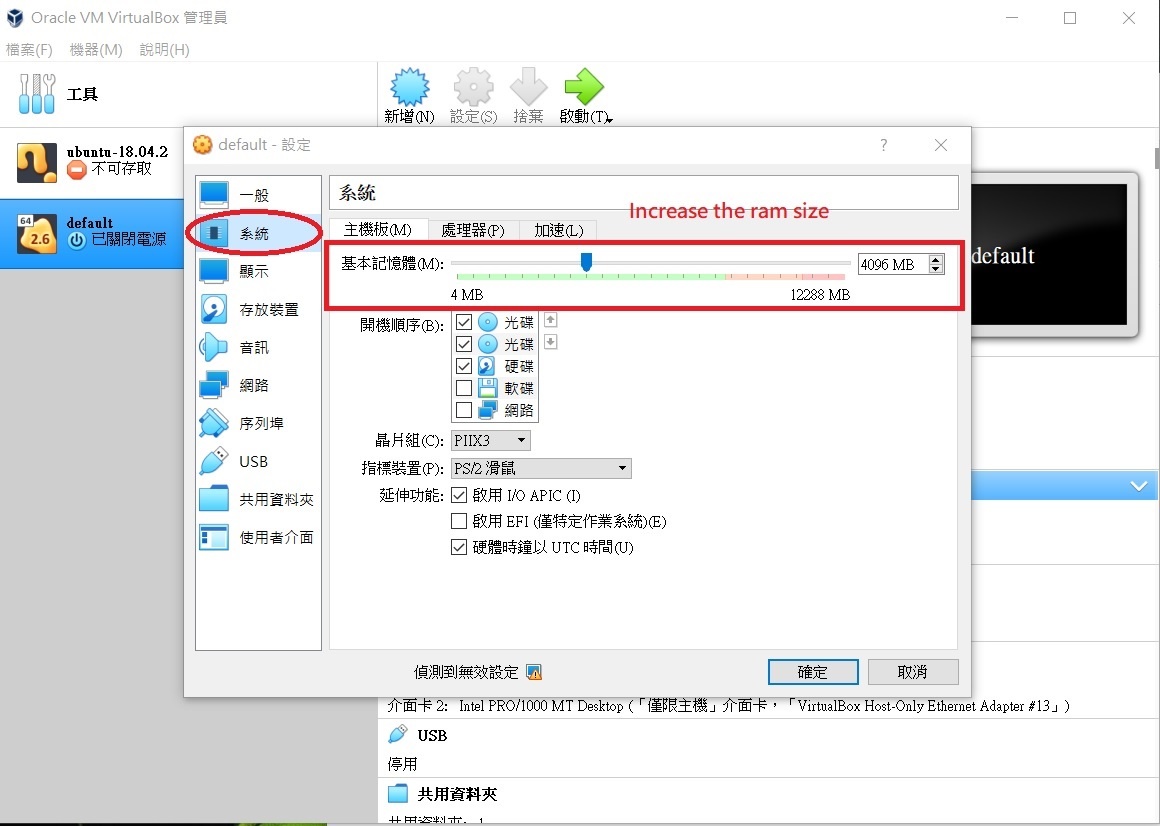
Figure FAQ3.4 VM settings
- Save the setting and restart the docker terminal. Now you can use more memory in your docker container.